Network Administrators can use port based access control to prevent unauthorized access to the corporate LAN. MAC-Based RADIUS is one method for providing this type of security. This article discusses the benefits of MAC-Based RADIUS and how to configure it in Microsoft NPS and Dashboard.
Note: RADIUS has been officially assigned UDP ports 1812 for RADIUS authentication and 1813 for RADIUS accounting by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). By default, NPS sends and receives RADIUS traffic by using User Datagram Protocol (UDP) ports 1812, 1813, 1645, and 1646. Windows Firewall on the NPS server is automatically configured with exceptions, during the installation of NPS, to allow this RADIUS traffic to be sent and received. This is the encryption key used for the handshake between Controller and NPS, and should be of high complexity. The standard port for RADIUS is 1812, and this is what NPS uses out of the box. Notably, make sure the RADIUS assigned VLAN options are checked so that you can specify VLANs based on policy in the NPS server.
Benefits of MAC-Based RADIUS
In some environments it is critical to control which devices can access the wired LAN. Ports in common areas make a network vulnerable to access by guests and other unauthorized users. MAC-Based RADIUS can be used to provide port based access control on your MS series switches. Unauthorized users are prevented from accessing to the wired LAN because each device that connects to a switch port will need to be authenticated before network access is granted. Devices are authenticated at the port level with MAC-Based RADIUS. When a device connects to a port with an access policy assigned, before network access is granted, the device must be authenticated by the RADIUS server. The switch (RADIUS client) sends a RADIUS Access-Request to the RADIUS server containing the username and password of the connecting device. The username and password combination is always the MAC address of the connecting device, lower case without delimiting characters. If a RADIUS policy exists on the server that specifies the device should be granted access and the credentials are correct, the RADIUS server will respond with an Access-Accept message. Upon receiving this message, the switch will grant network access to the device on that port. If the RADIUS server replies with an Access-Reject because the device does not match a policy, the switch will not grant network access. It is possible however, to configure the switch to drop devices into a Guest VLAN when they fail to authenticate. The Guest VLAN would provide Internet access only. Below is an example of a basic MAC-Based authentication exchange.
Adding MS Switches as RADIUS clients on the NPS Server

All switches that that need to authenticate connecting devices must be added as RADIUS clients on in NPS. Below are the steps to add the switches as RADIUS clients.

1) Open the NPS Server Console by going to Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > Network Policy Server.
2) In the Left pane, expand the RADIUS Clients and Servers option.
3) Right click the RADIUS Clientsoption and select New.
4) Enter a Friendly Name for the MS Switch.
5) Enter the the IP Addressof your MS Switch.
6) Create and enter a RADIUS Shared Secret (note this secret - we will need to add this to the Dashboard).
7) Press OKwhen finished.
8) Repeat these steps b - g for all switches. See Figure 1 for a sample RADIUS client configuration.
Figure 1.
Create a user account in Active Directory for a connecting device.
1) Open Active Directory Users and Computers: Start > All Programs > Administrative Tools > Active Directory Users and Computers.
2) Create a new user account. the username and password should be the MAC address of the connecting device (letters need to be lower case and it should not have any delimiting characters). See Figure 2 for example user account.
Figure 2.
Configuring a NPS Connection Request Policy.
1) In the NPS Server Console, navigate to NPS (Local) > Policies > Connection Request Policies.
2) Right click on Connection Request Policies, and select New.
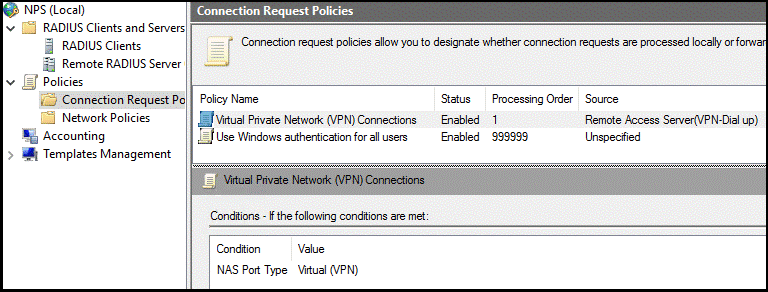
3) Name the policy and select Next.
4) On the Specify Conditions page add the following condition: NAS port type as Ethernet (Figure 3) followed by clicking Next.
5) Click Next on the Specify Connection Request Forwarding screen.
6) Click Next on the Specify Authentication Methods screen.
7) Click Next on the Configure Settings screen.
8) Review settings and click Finish on the Completing Connection Request Policy Wizard screen.
Figure. 3
Configuring a NPS Network Policy.
1) In the NPS Server Console, navigate to NPS (Local) > Policies > Network Policies.

2) Right click on Network Policies, and select New.
3) Name the policy and select Next. (Figure 4)
Figure 4.
4) On the Specify Conditions page add the following two conditions Windows Groups, this can be the group containing especially for the user accounts created in Part 3. See KB Creating a Windows Group For MAC Based Authentication. For our example we will use DOMAINNAMEDomain Users. Then specify NAS port type Ethernet followed by clicking Next. (Figure 5)
Figure 5.
5) Click Next on the Specify Access Permission screen.
6) On the Configure Authentication Methods page, uncheck all options except Unencrypted authentication (PAP, SPAP). (Figure 6)
Figure 6.
7) Click Next on the Configure Constraints screen.
8) Click Next on the Configure Settings screen.
Troubleshooting Nps Radius
9) Review settings and click Finish on the Completing New Network Policy screen. (Figure 7)
Figure 7.
Creating a MAC-Based RADIUS Access Policy in Dashboard.
1) On the Dashboard navigate to Configure > Access Policies.
2)Click on the link Add Access Policy in the main window then click the link to Add a server.
3)Enter the IP address of the RADIUS server, the port (default is 1812 or 1645), and the secret you created above in part 2. (Figure 8)
4) Click Save changes.
Figure 8.
Apply Access policy to MS Switchports
1) On the Dashboard navigate to Configure > Switchports.
2) Select the port(s) that should have the policy applied.
3) Click the Edit button, make sure the port type is Access, and from the Access policy drop-down select the policy that was created in part 5.
(Figure 9)
Figure 9.
In this article I will go through the steps required to implement RADIUS authentication using Windows NPS (Network Policy Server) so that firewall administrators can log-on using domain credentials.
My Setup
- Palo Alto running PAN-OS 7.0.X
- Windows Server 2012 R2 with the NPS Role – should be very similar if not the same on Server 2008 and 2008 R2 though
- I will be creating two roles – one for firewall administrators and the other for read-only service desk users.
NPS Configuration
First we will configure the NPS server.
- Create the RADIUS clients first. The clients being the Palo Alto(s). If you have multiple or a cluster of Palo’s then make sure you add all of them. You don’t want to end up in a scenario where you can’t log-in to your secondary Palo because you forgot to add it as a RADIUS client. Make a note of the generated secret key as you will need it later on.
- Next create a connection request policy if you don’t already have one. A connection request is essentially a set of conditions that define which RADIUS server will deal with the requests. In my case the requests will come in to the NPS and be dealt with locally.
- Now we create the network policies – this is where the logic takes place.
Now let’s configure the Palo…

Windows Server 2016 Nps Radius
Palo Configuration
First we will configure the Palo for RADIUS authentication. This involves creating the RADIUS server settings, a new admin role (or roles in my case) and setting RADIUS as the authentication method for the device.
Note: Don’t forget to set the Device –> Authentication Settings –> Authentication Profile on all your Palo’s as the settings on these pages don’t sync across to peer devices.
Other tips
- It is good idea to configure RADIUS accounting to monitor all access attempts
- Change your local admin password to a strong, complex one
- Monitor your Palo system logs if you’re having problems using this filter:
[code]( eventid eq auth-success ) or ( eventid eq auth-fail )[/code]
Related posts:
